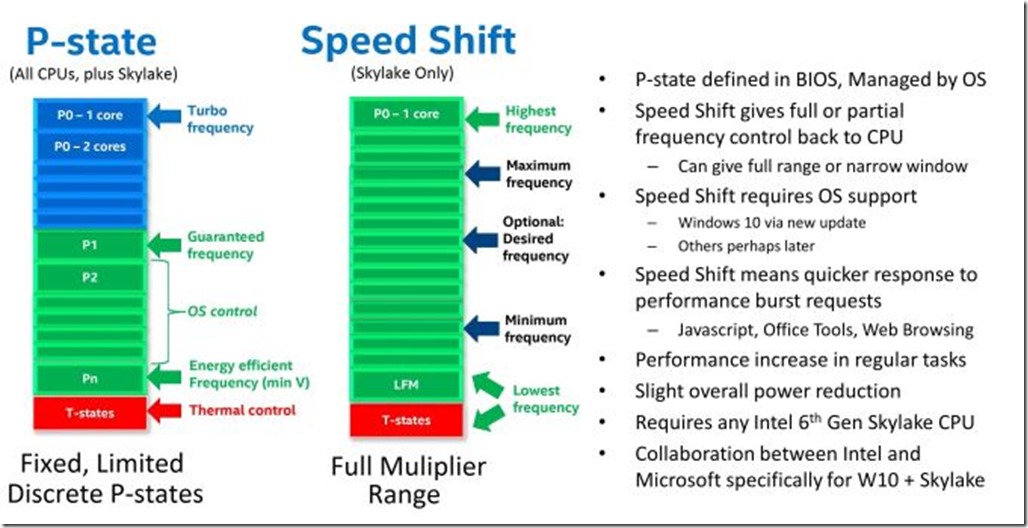
Back in 2015, as part of the Skylake architecture, Intel released a new processor feature called Intel Speed Shift. This is an improved version of Intel SpeedStep, which you may have heard of since it has been around much longer. Essentially, Speed Shift allows the processor and the operating system to cooperate better, and more quickly “throttle up” the clock speed of the processor cores in response to an increased workload.
With the older SpeedStep technology, it would typically take 100-150ms for a processor core to fully ramp up its clock speed in response to a lower P-state. With Speed Shift, this delay goes down to 30-35ms to fully ramp up.
Figure 1: Intel Speed Shift
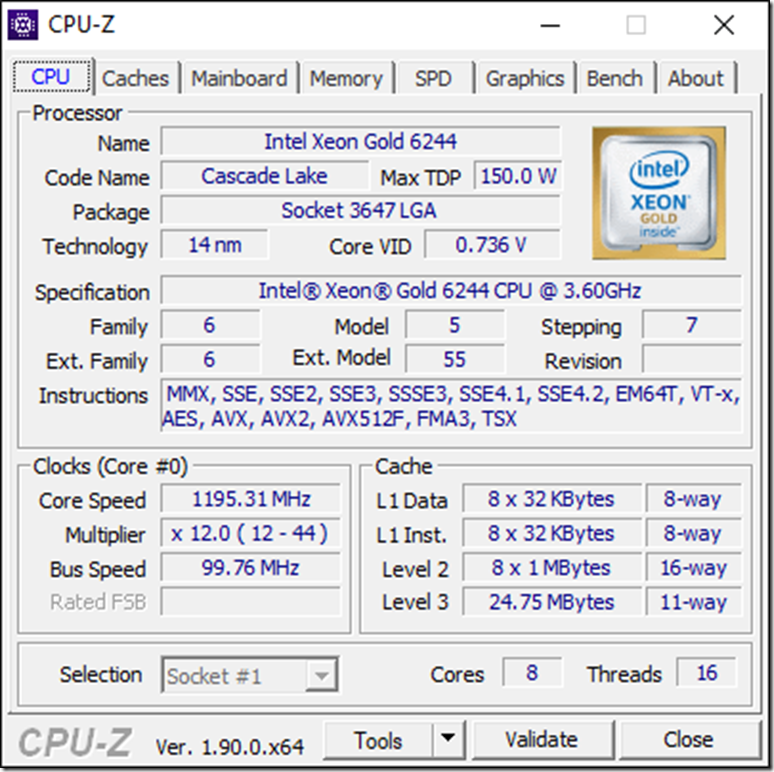
This technology has been in Intel desktop and mobile processors since Q3 2015 (although you couldn’t use it until Microsoft patched Windows 10 in November 2015). It showed up in Intel server processors in the Skylake-SP family and in the current Cascade Lake-SP family. Figure 2 shows a current Intel Xeon Gold 6244 processor which has Intel Speed Shift support (although you can’t actually tell from CPU-Z).
Figure 2: Intel Xeon Gold 6244 in CPU-Z
Remember, you need a new enough processor (Skylake or newer) and operating system support in order to enable Intel Speed Shift. This means a new enough build of Windows 10, Windows Server 2016 or Windows Server 2019.
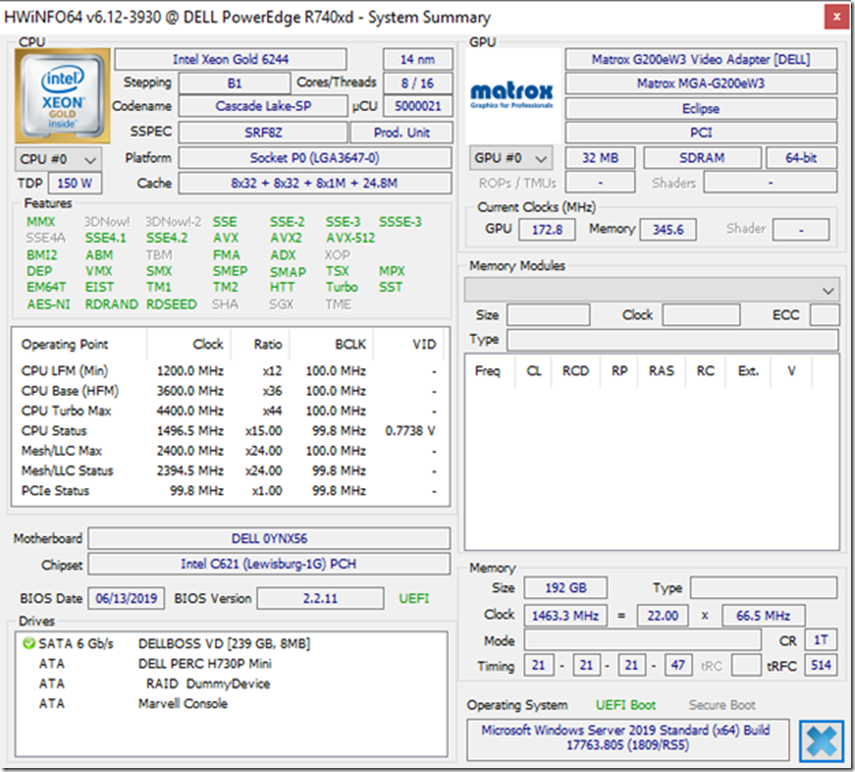
One way to confirm whether Intel Speed Shift is enabled is to use the free HWiNFO64 utility. On the main HWiNFO screen, in the CPU section, there is a Features section that shows various AMD and Intel processor features. They will be green if that feature is enabled on your system, and greyed out if it is not.
The one for Intel Speed Shift is SST, at the bottom right of the section. You can see this feature enabled in Figure 3.
Figure 3: HWiNFO64 Showing Intel Speed Shift Enabled
SST is something you want to have enabled on your database server if at all possible. If you have the two main prerequisites, you may still have to poke around in your BIOS settings to make sure this ends up being enabled. If you don’t see it enabled in HWiNFO64, you might want to bug your server vendor to find out what combination of BIOS settings are required your your model server.

4 thoughts on “Checking To See If Intel Speed Shift Is Enabled”
Yikes, Glenn! So glad you publish this stuff… Q is, why wouldn’t Dell have the correct BIOS settings out of the gate for a Skylake-SP 740XD chassis equipped with 6144 CPUs? Retrofitting BIOS settings now, to get what we paid for. THANKS for making us aware.
Glad to help!
Hi Glen,
Just to clarify – you are saying that the performance impact of previous versions of Speed Step have been mitigated (where the advice was to disable), and Speed Shift is now going to improve performance?
In the case of a long set of single row inserts all performed on the same SPID – will this be faster or slower with Speed Shift enabled?
SpeedStep will vary your clock speed up and down (mostly down) in response to your workload to try to minimize energy usage. Speed Shift just lets the CPU have more direct control from the OS to throttle up more quickly. There is no performance downside from Speed Shift. The performance impact will be fairly low in most situations, but it will always be positive. We might as well take advantage of this feature if possible.